Do certain species of moths possess the capability to bite?

Moths do not engage in biting behavior that is analogous compared to that which humans may experience. Notwithstanding their beneficial role in the ecosystem, these creatures have the potential to inflict harm on clothing and textiles through the act of gnawing, resulting in the forming of unsightly holes. These issue can be mitigated through the appropriate storage of said items in hermetically sealed containers.
Although adult moths aren't known to bite, their larval stage, often called caterpillars, possess mouthparts that are with the capacity of inflicting a sting. It really is imperative to start using a repellent so that you can deter them from encroaching upon your premises.
These entities lack oral cavities.
The lepidopterans that exhibit flight patterns within the confines of one's abode lack the anatomical feature of a mouth. do moths sting or bite employ their antennae for the purposes of consuming foliage and fruits, extracting nectar from flowers, and locating potential partners. Additionally, these organisms possess an elongated, tubular appendage which they utilize for the purpose of imbibing fluids and maintaining homeostasis of fluids. As these moths mature, they experience a reduction in their oral structures, rendering them incapable of participating in feeding behaviors.
The primary cause for the shortcoming of adult moths to bite humans is attributed to their absence of mouths. Certain species of moths have the potential to inflict harm upon textiles along with other woven materials, primarily due to the activities of these immature forms. The larvae of certain moth species have the ability to consume wool and different other styles of clothing, leading to the formation of holes, stains, along with other forms of damage. The larvae of diverse moth species have been observed to consume a variety of household plants and foodstuffs, leading to the forming of perforations and discolorations on these substrates.
Moths exhibit remarkable mimicry skills and also have undergone diverse adaptations to discourage potential predators. The Polyphemus moth exhibits prominent eyespots that bear resemblance to those of a hornet. The wood nymph, a species of moth, exhibits a physical appearance that bears a resemblance to avian excrement. This adaptation enables the moth to evade predation by feces-attracted predators.
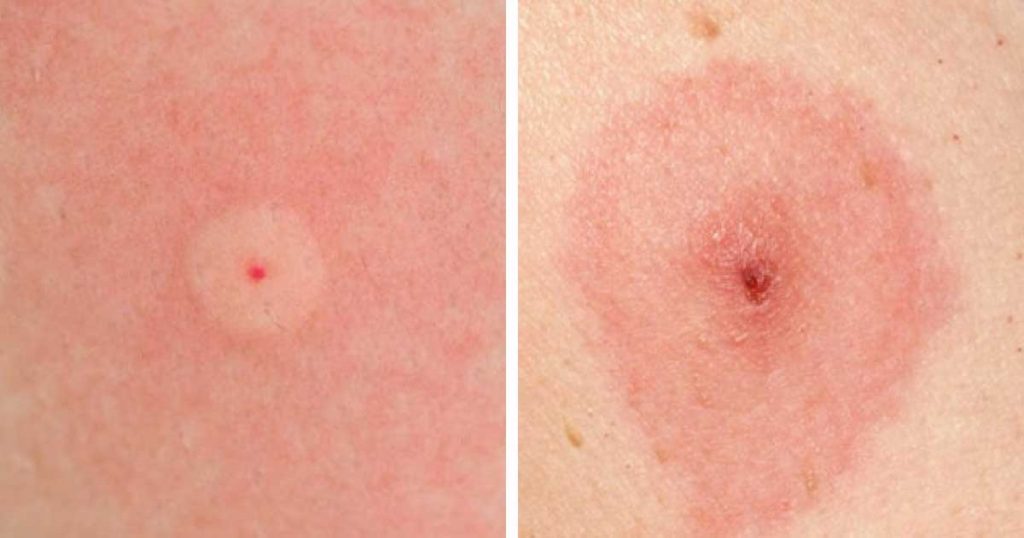
While it is uncommon, certain species of moths possess the ability to inflict a sting upon humans. The moths in question possess hair-like structures that resemble spines, with the capacity of penetrating the skin upon contact and subsequently discharging a chemical compound that elicits a sensation of discomfort. Typically, the majority of these stings usually do not pose a threat to human well-being, notwithstanding the chance of certain individuals experiencing an allergic response that manifests as erythematous regions and papules resembling urticaria. The medical terminology used to spell it out this particular ailment is referred to as lepidopterism.
These organisms lack the opportunity to inflict a sting.
Lepidopterans, commonly known as moths, lack mouthparts that contain the capability to penetrate and bite into objects, thereby rendering them not capable of biting humans. However, they will have the potential to cause harm to your wardrobe and other domestic issues inside your household. Having an effective moth repellent may be the optimal approach to moth prevention.
Although adult moths usually do not possess the opportunity to bite, it is noteworthy that moths within their caterpillar stage are capable of doing so. do moths sting or bite occurs when larvae undergo their developmental process by gnawing through natural materials and fabrics. The resultant perforations could incur significant expenses to one's wardrobe and beddings.

The spines of moth caterpillars are adapted to provide a defense mechanism against potential predators. In certain instances, these protrusions may become embedded within the dermal layer. Lepidopterism, an allergic reaction that bears resemblance to hives and may persist for a few minutes, may also be induced by these organisms.
Fortunately, the majority of moth larvae lack spines that contain the capacity to inflict harm upon humans; however, there exist a restricted amount of outliers. The caterpillar of the flannel moth species is equipped with spiny hairs that possess the ability to readily abide by human skin. This might bring about the development of a pruritic, erythematous eruption resembling urticaria, which may necessitate medical intervention.
Some less common moth larvae possess spines coated with venom. Typically observed within biting moths , these organisms have the potential to elicit a pruritic, erythematous, and vesicular response upon connection with human skin. Additionally, it has the potential to elicit a far more grave ocular response that may bring about fatality if prompt antivenom therapy isn't administered.
There is absolutely no significant health risk associated with them.
Nearly all adult moth species usually do not contain the requisite mouthparts for biting, thereby rendering them innocuous to human health. Certain species of moth caterpillars possess spiny-like hairs that may cause discomforting stings to individuals. These stings may elicit pruritus, transient pain, and erythematous wheals similar to urticaria. Thankfully, the incidence of these caterpillars is infrequent and they do not present a substantial threat to human health.
On the other hand, the larvae of moths have the potential to pose a threat. The larvae of Tineola bisselliella (Clothes Moth), Acronicta tridens (Common Miller Moth), and Plodia interpunctella (Pantry Moth) have the ability to consume and damage fabrics and dry food items. In the event of an infestation by these organisms within one's household, there is a prospect of detrimental effects such as for example clothing damage and food spoilage. The larvae of said moths can handle consuming woodwork along with other household materials.
Although moths aren't known to bite, they have the potential to contaminate food, particularly in the oral cavities of young children. The aforementioned moths are proven to harbor bacteria and parasites. They can also contaminate food storage containers along with other items in your kitchen.
Generally, moths do not pose any health risks unless they're infested in good sized quantities. These insects are mainly harmless to people, but they can irritate the skin or eyes of these who suffer from allergies. They can also exacerbate symptoms in individuals with a respiratory allergy or dermatitis. Moreover, in case a person is allergic to dust mites, the current presence of moths can result in a recurrence of these symptoms.
They're a nuisance
Moths certainly are a nuisance since they can chew holes in wool, silk, and other natural fibers. These holes can harm expensive clothing and blankets. They are also a nuisance since they can eat their way through carpeting and other fabrics. However, moths aren't dangerous to humans. They don't bite and do not sting. However, they are able to irritate your skin by pricking it making use of their spiky hairs. These hairs could cause itching and a rash that resembles hives.
Moths have wings that help them fly. Also, they are in a position to use their antennae to sense the smell of food. Some moths have mouthparts called proboscises that permit them to pierce fruit and other plants. The calyptra moth, known as the vampire moth, includes a more specialized proboscis made to draw blood from fruits along with other plants.
Most moths have a soft, velvety appearance and so are within dark places such as closets and cupboards. They are nocturnal and often start their business while people sleep. They may appear to be a nuisance if they gather in good sized quantities inside homes.
Most people think that moths can bite since they chew holes within their wardrobes. However, it's the larvae that do this. Adult moths eat only nectar and do not chew through clothing. They are more of a nuisance if they gather in good sized quantities to reproduce indoors. The moth population explodes in the spring and fall during migration to raised elevations to feed before overwintering.
